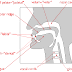
A dental consonant is a consonant articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as /t/, /d/, /n/, and /l/ in some languages. Dentals are primarily distinguished from sounds in which contact is made with the tongue and the gum ridge, as in English (see Alveolar consonant),
due to the acoustic similarity of the sounds and the fact that in the
Roman alphabet they are generally written using the same symbols (t, d, n, and so on).
Examples:
/d/:
Tongue tip: Firmly pressed against gum ridge behind upper front teeth.
Airstream: Stopped and then exploded.
Vocal cords: Vibrating.
Tongue tip: Firmly pressed against gum ridge behind upper front teeth.
Airstream: Stopped and then exploded.
Vocal cords: Vibrating.
/n/:
Tongue: Firmly pressed against gum ridge behind upper front teeth.
Airstream: Continuous through the nose.
Vocal cords: Vibrating






0 comments: